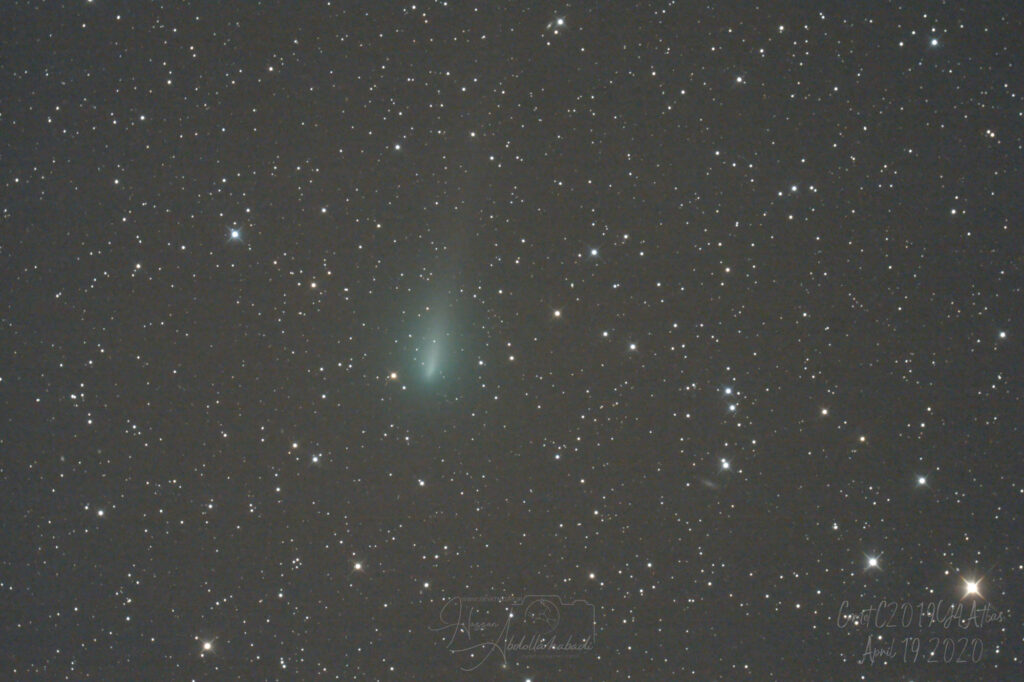
Comet C/2019 Y4 (ATLAS) was discovered on December 28, 2019, with a 0.5 m (20 in) reflecting telescope atop Mauna Loa in Hawaii.The images were taken as part of the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS).
At the time of its discovery, the comet shone at magnitude 19.6 in the constellation Ursa Major as viewed from Earth.Larry Denneau was the first to identify the object’s cometary appearance,placing the object on the Minor Planet Center’s Possible Comet Confirmation Page, alerting other astronomers. Further observations over subsequent days identified a coma; a comet tail became increasingly apparent as observations continued.
C/2019 Y4 (ATLAS) was a comet with a near-parabolic orbit, Early predictions based on the brightening rate suggested that the comet could become as bright as magnitude 0 matching the brightness of Vega.
It received widespread media coverage due to its dramatic increase in brightness and orbit similar to the Great Comet of 1844, but on 22 March 2020, the comet started disintegrating.Such fragmentation events are very common for Kreutz Sungrazers. The comet continues to fade and did not reach naked eye visibility.
C/2019 Y4 (ATLAS) was the brightest on March 30 when it had an apparent magnitude of about 7, but after disintegrating, it continued to fade, until it was last observed on May 21. It is located in the constellation Monoceros but is no longer visible. It reached its nearest point to Earth on May 23 and come to perihelion (closest to the Sun) on May 31.
In April 2020, astronomers reported, on The Astronomer’s Telegram, the possible disintegration of Comet ATLAS.The comet has fragmented into at least 4 pieces.NASA subsequently reported that the Hubble Space Telescope has identified that there could be as many as roughly “30 fragments on April 20, and 25 pieces on April 23.
Type : Comet
Optic : GSO 8’’ RC
Focal Length :1072 mm
Mount : Sky-Watcher AZ-EQ6
Camera : Canon EOS 60Da
ISO : 12800
Filters : –
Guide Scope : Yes
Total EXP : 30*45 Sec
Technique used : –
Dark : Yes
Flat : –
Bias : –
Dark Flat : –
Software : DeepSky Stacker , Photoshop
Date Taken : 19 April 2020
Place : Akbar Abad Village , Rivash , Iran
دنباله دار اطلس
دنبالهدار اطلس در ۷ دی ۱۳۹۸ با یک تلسکوپ بازتابی ۰.۵ متری (۲۰ اینچی) بر فراز مائونا لوا در هاوایی کشف شد. این تصاویر به عنوان بخشی از سیستم هشدار آخرین برخورد سیارک زمینی (اطلس) گرفته شده است
در زمان کشف، این دنبالهدار با قدر ظاهری ۱۹.۶ در صورت فلکی دب اکبر از زمین دیده میشد. لری دنو اولین کسی بود که ظاهر دنبالهدار این جرم را شناسایی کرد و آن را در صفحه تأیید دنبالهدارهای احتمالی مرکز سیارات کوچک قرار داد و به سایر ستارهشناسان هشدار داد. مشاهدات بیشتر در روزهای بعد، یک کما را شناسایی کرد. با ادامه مشاهدات، دم دنبالهدار به طور فزایندهای آشکار شد
اطلس دنبالهداری با مدار تقریباً سهموی بود. پیشبینیهای اولیه بر اساس نرخ روشنایی نشان میداد که این دنبالهدار میتواند به اندازه قدر ظاهری ۰، معادل درخشندگی وگا، درخشان شود. این دنبالهدار به دلیل افزایش چشمگیر روشنایی و مداری مشابه دنبالهدار بزرگ ۱۸۴۴، پوشش رسانهای گستردهای را به خود اختصاص داد، اما در ۳ فروردین ۱۳۹۹، این دنبالهدار شروع به فروپاشی کرد. چنین رویدادهای تکهتکه شدن برای دنبالهدار کروتز سانگرازر بسیار رایج است. این دنبالهدار همچنان در حال محو شدن است و به دید چشم غیرمسلح نمیرسد
اطلس در ۱۱ فروردین با قدر ظاهری حدود ۷، درخشانترین بود، اما پس از فروپاشی، همچنان در حال محو شدن بود تا اینکه آخرین بار در ۱ خرداد ۱۳۹۹ مشاهده شد. این دنبالهدار در صورت فلکی تکشاخ قرار دارد اما دیگر قابل مشاهده نیست. این دنبالهدار در ۳ خرداد به نزدیکترین نقطه خود به زمین رسید و در ۱۱ خرداد ۱۳۹۹ به حضیض خورشیدی (نزدیکترین فاصله از خورشید) رسید
دراردیبهشت ۱۳۹۹، ستارهشناسان در تلگرام اخترشناسان از احتمال فروپاشی دنبالهدار اطلس خبر دادند. این دنبالهدار حداقل به ۴ قطعه تقسیم شده است. ناسا متعاقباً گزارش داد که تلسکوپ فضایی هابل شناسایی کرده است که ممکن است در ۱ اردیبهشت ۱۳۹۹ تقریباً «۳۰ قطعه» و در۴ اردیبهشت «۲۵ قطعه» وجود داشته باشد